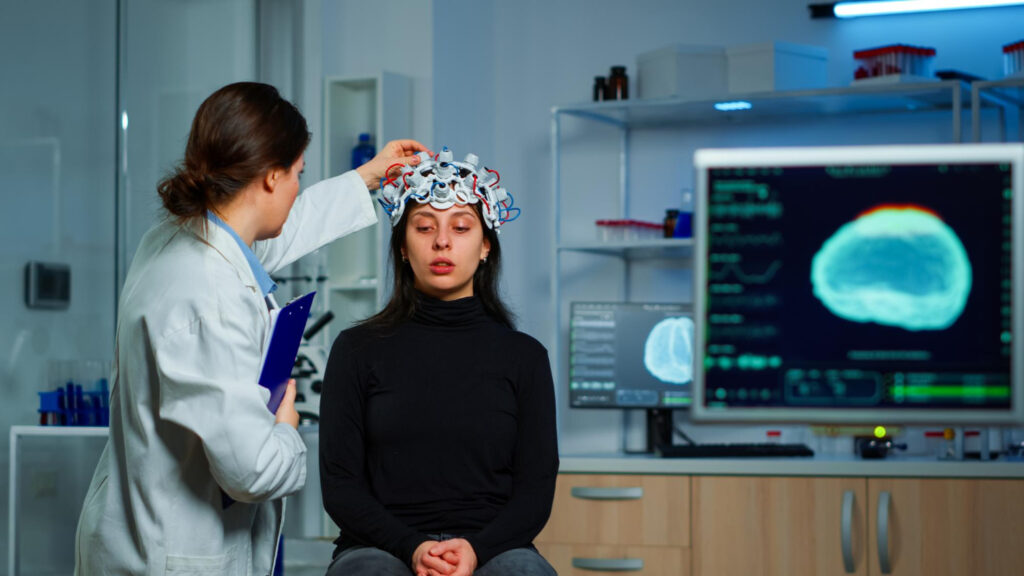
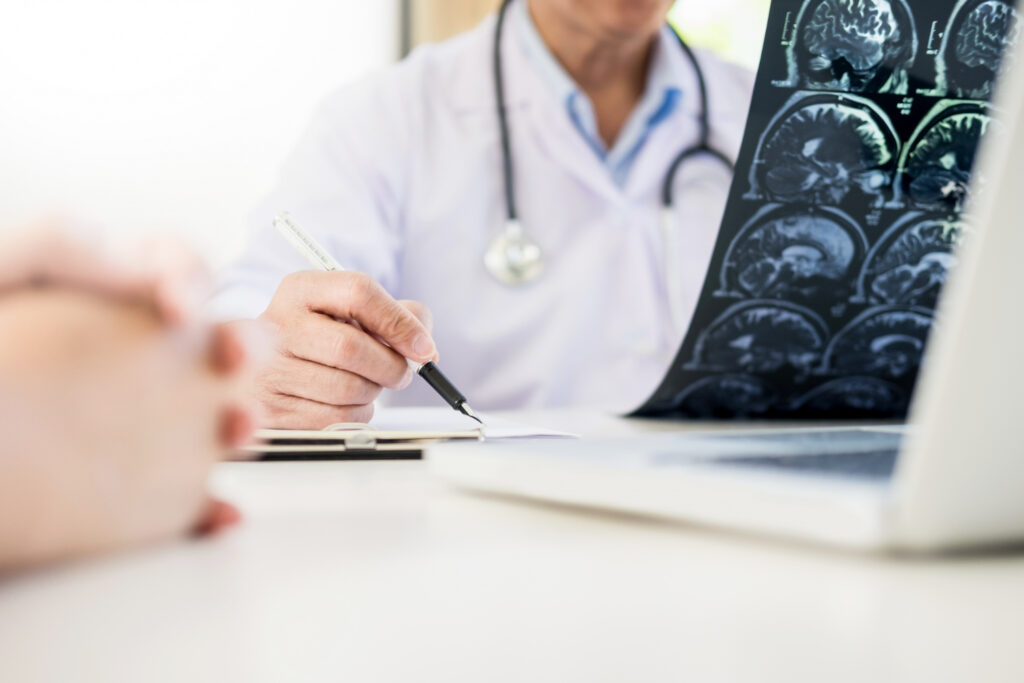
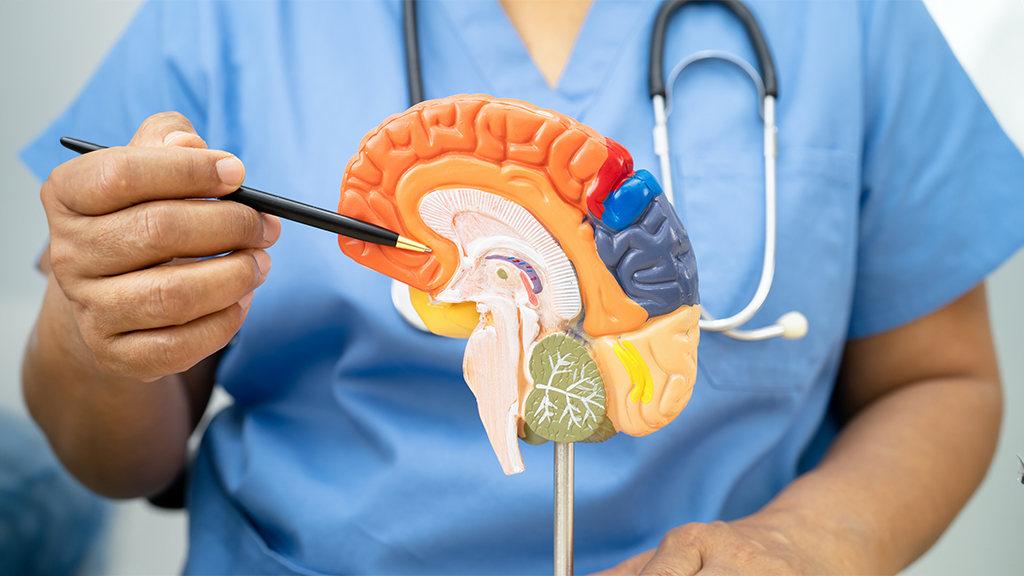
The management of epilepsy and seizures involves a comprehensive approach to control and reduce the frequency and severity of seizures, improving the quality of life for patients. Treatment strategies may include a combination of medications, lifestyle adjustments, and in some cases, surgical interventions, tailored to the individual’s specific condition.
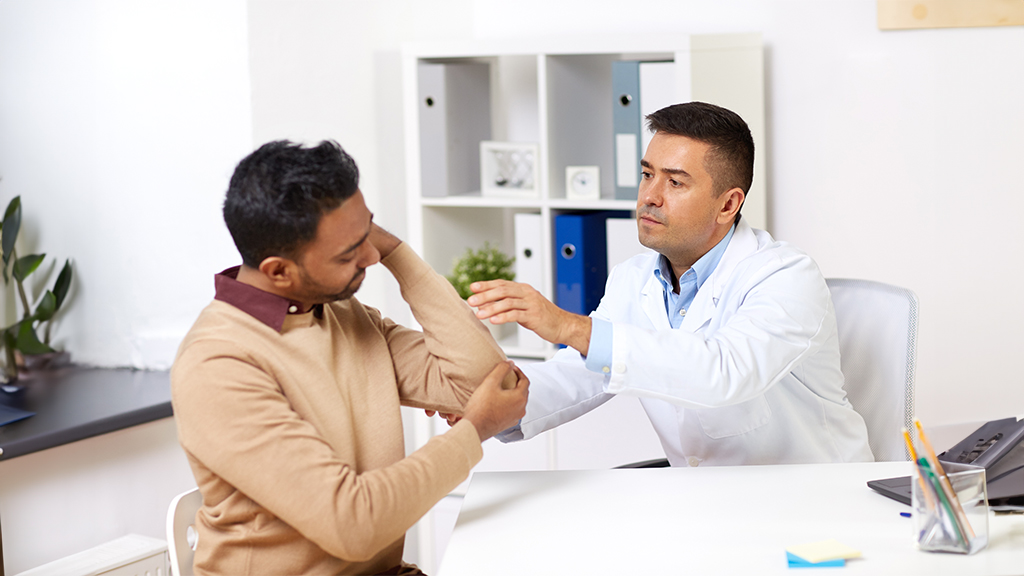
Neuropathy, or nerve damage, often leads to chronic pain, tingling, numbness, and weakness in affected areas, typically in the hands, feet, or limbs. It can result from various causes, including diabetes, infections, injuries, or even certain medications. Nerve pain can be debilitating, affecting daily activities and overall quality of life.
Effective neuropathy and nerve pain care aim to manage symptoms, prevent further damage, and improve the patient’s ability to function. Treatment may involve medication to relieve pain and inflammation, such as anticonvulsants, antidepressants, or topical treatments. Additionally, physical therapy can help improve strength and mobility while addressing any loss of sensation.
Advanced techniques like nerve blocks, electrotherapy, or even regenerative treatments like PRP (Platelet-Rich Plasma) therapy may be recommended for certain cases. Lifestyle changes, such as improved nutrition, regular exercise, and stress management, also play a significant role in managing neuropathy and nerve pain.
A comprehensive approach to care ensures the best outcomes, helping patients regain their quality of life and live with less discomfort. Early intervention and customized treatment plans are key to managing nerve pain effectively.
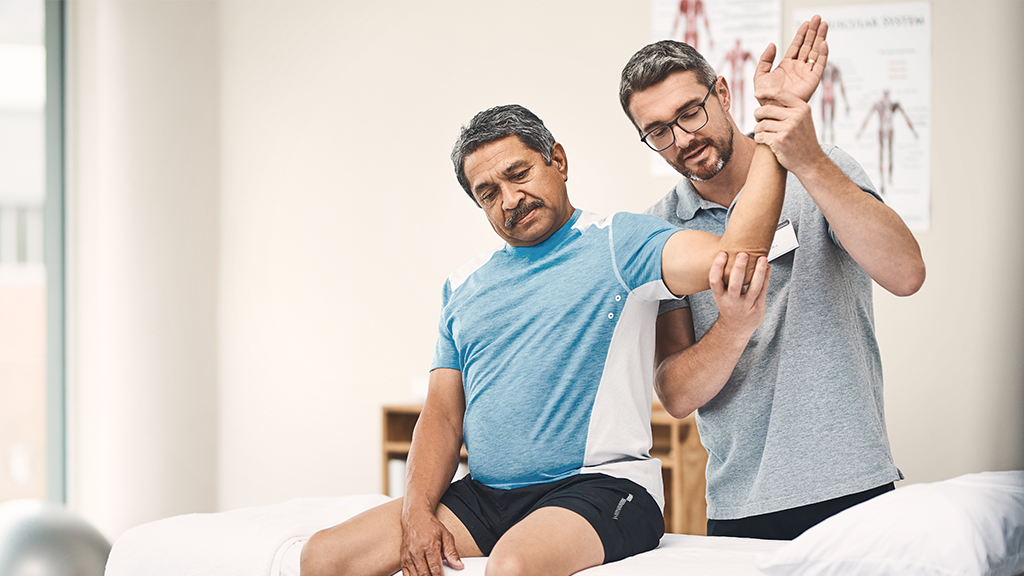
Movement disorders, such as Parkinson’s disease and dystonia, are neurological conditions that cause abnormal movements and affect a person’s ability to control their body. Parkinson’s disease is a progressive condition that affects movement, leading to tremors, rigidity, bradykinesia (slowness of movement), and postural instability. Dystonia, on the other hand, causes involuntary muscle contractions, leading to twisting, repetitive movements, or abnormal postures.
Effective treatment for movement disorders focuses on alleviating symptoms, improving mobility, and enhancing the patient’s quality of life. Therapies may include medication, such as dopamine replacement therapy for Parkinson’s, to help control motor symptoms. Botulinum toxin injections (Botox) are commonly used to treat dystonia by reducing muscle contractions.
For patients with advanced conditions, deep brain stimulation (DBS) may be considered. DBS involves implanting electrodes in the brain to help regulate abnormal brain activity and alleviate symptoms of Parkinson’s and dystonia.
Physical therapy and occupational therapy are essential in helping patients maintain movement, improve flexibility, and manage daily activities. Speech therapy may also be beneficial for those with speech and swallowing difficulties.
A multidisciplinary approach, including medication, therapy, and advanced treatments, ensures optimal care for those with movement disorders, empowering them to lead more independent, fulfilling lives.
Headaches and migraines can severely impact daily life. Migraines are often intense, throbbing pains, usually on one side of the head, accompanied by nausea and sensitivity to light or sound. Tension headaches are more common and cause dull, persistent pain around the head.
Management involves a combination of medication, lifestyle changes, and preventive strategies. Pain-relieving medications like NSAIDs and triptans help alleviate symptoms, while preventive treatments such as beta-blockers or anticonvulsants can reduce frequency.
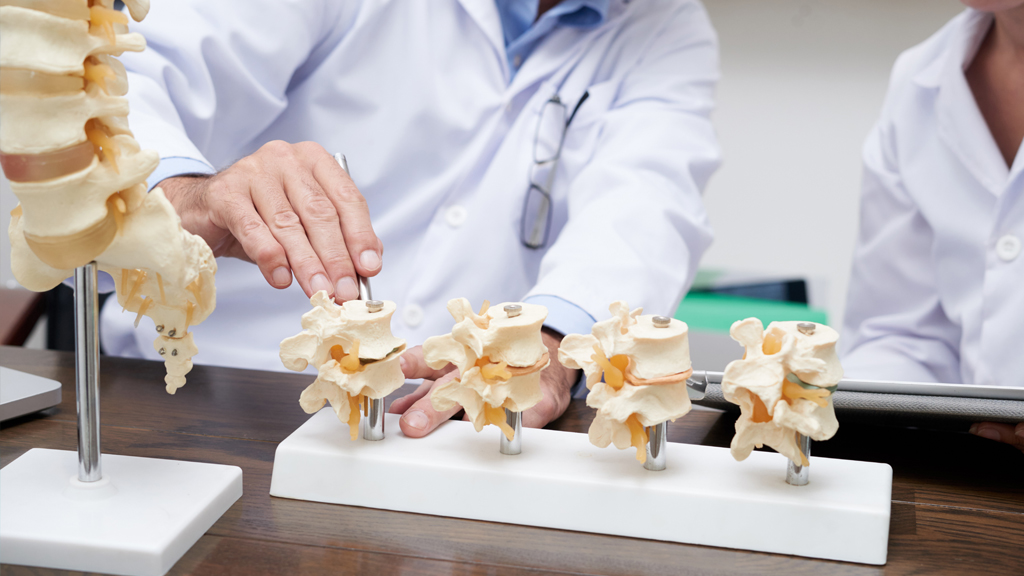
Spinal cord disorders refer to conditions that affect the spinal cord’s function, potentially leading to neurological impairments such as weakness, numbness, or paralysis. These disorders can result from various causes, including trauma, infections, tumors, or degenerative diseases.
Conditions such as spinal cord injury, multiple sclerosis, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) impact the nerve pathways, disrupting communication between the brain and the body. Symptoms vary, from localized pain and muscle weakness to full-body paralysis, depending on the location and severity of the damage.
Conditions such as spinal cord injury, multiple sclerosis, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) impact the nerve pathways, disrupting communication between the brain and the body. Symptoms vary, from localized pain and muscle weakness to full-body paralysis, depending on the location and severity of the damage.
Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial in managing spinal cord disorders. Treatment options include medication to manage pain or inflammation, physical therapy to maintain mobility, and, in some cases, surgical intervention to address underlying issues such as spinal cord compression. Advanced therapies like stem cell treatment and neurorehabilitation are emerging as promising options to promote recovery and improve functionality.
A comprehensive treatment approach, involving medical, physical, and psychological care, can significantly enhance the quality of life for those affected.
Infections of the brain and peripheral nervous system can be caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi, or parasites, leading to conditions that severely impact neurological function. These infections can result in conditions such as meningitis, encephalitis, and peripheral neuropathy.
Meningitis is the inflammation of the protective membranes covering the brain and spinal cord, often caused by bacterial or viral infections. Symptoms may include fever, headache, neck stiffness, and confusion. Encephalitis, the inflammation of the brain itself, is typically caused by viral infections and can lead to seizures, cognitive impairment, and motor dysfunction.
Peripheral nervous system infections affect the nerves outside the brain and spinal cord, leading to conditions like Guillain-Barré syndrome or viral infections such as shingles. These conditions can cause weakness, pain, and loss of sensation in the affected areas.
Treatment typically involves a combination of antiviral, antibacterial, or antifungal medications, depending on the cause. Early diagnosis and appropriate intervention are critical to minimize the risk of long-term neurological damage. Supportive care, including pain management and physical therapy, may also be required to aid recovery.